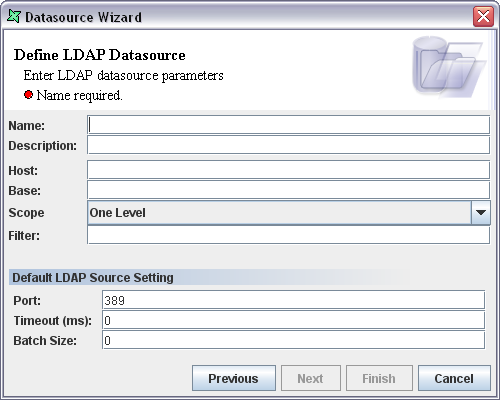
The LDAP DataSource Wizard is shown in Figure 11.1, “LDAP DataSource Wizard”.
Name: Enter the DataSource name in the text box. This should be a unique name.
Description: Any extra description that is used to describe the data source can be entered in the Description text box.
Host: The host name or IP address of the server is specified here.
Base: The Base, sometimes called Distinguished Name (DN) is used to uniquely identify entries in LDAP. The base is always a fully qualified name that identifies entries starting from the root of the LDAP name space (as defined by the server).
The following string-type attributes represent the set of standardized attribute types for accessing an LDAP directory. The Base can be composed of attributes using the LDAP syntax. For example:
CN - CommonName
L - LocalityName
O - OrganizationName
OU - OrganizationalUnitName
C - CountryName
STREET - StreetAddress
If there are domain components com and
example, then the base for the com.example
domain is "dc=com,dc=example". Similarly, if the organizational
unit comes under the domain com.example, then to access
people within the organization you would use
"ou=people,dc=example,dc=com".
Scope: Scope defines the set of information used to search for data. You may choose one of three values: Object, One Level or Subtree. Choosing Object will only return data held by the object identified by the Base. Choosing One Level will return data held by children of the object identified by the Base (this is the default). Finally Subtree will return data from all children in the subtree below the Base.
Filter: Search filters enable you to define criteria for more efficient and effective searches. LDAP filters are used to specify criteria for directory search. Filters are optional - if you leave it blank a default filter "objectclass=*" will be used.
In filter, the matchingAttrs argument is converted into a string filter that is a conjunctive expression of the attributes from matchingAttrs.
For example, when a matchingAttrs containing the attributes sn:Geisel and mail: (no value given), it is translated into the string filter "(&(sn=Geisel)(mail=*))".
The filter conventions are given in the ftp://ftp.isi.edu/in-notes/rfc2254.txt link.
Port: The default port for connection is 389. The LDAP port number of the machine on which the Directory Services is running is specified in the text box.
Timeout: This is the time interval allowed for certain operation to occur. The LDAP timeout is the time limit required to wait for the result. If 0 is specified then it means that the datasource will wait indefinitely.
Batch Size: The value of the batch size property specifies the batch size of the search results returned by the server. The batch size is specified in the Batch Size text box. A setting of 0 means that the provider should block until all the results have been received. If for instance the batch size is specified as 24 then the provider should block until 24 entries have been read from the server or until the enumeration terminates, whichever produces fewer number of results.
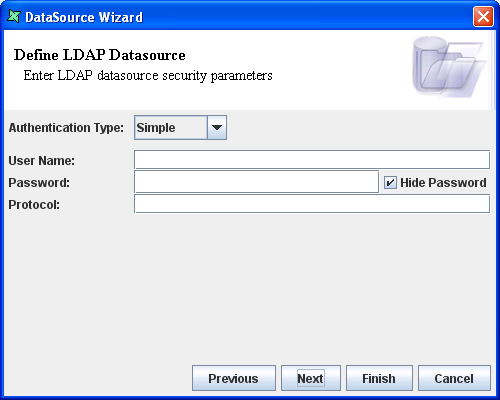
On clicking the Next button, the LDAP Security page will appear. In Figure 11.2, “Security Parameters”, the default type "none" has been changed to "simple" so that you can see the available options. If your server doesn't require any authentication for read access, you can leave the authentication type as none.
Authentication Type: The value of this property is a string that specifies the authentication mechanism(s) for the provider to use. The following values are defined for this property:
none: If this option is selected from the combo box, then no authentication is required. It is referred to as anonymous bind.
simple: If this option is selected then a clear text password is used. This type of bind sends an unencrypted user name and password to the LDAP server for verification, and can be secured only by using a secure channel to transmit the password, e.g. SSL.
GSSAPI: GSSAPI stands for Generic Security Services Application Programming Interface. An application level interface (API) to system security services. It provides a generic interface to services which may be provided by a variety of different security mechanisms.
Digest-MD5: In Digest-MD5, the LDAP server sends data that includes various authentication options that it is willing to support plus a special token to the LDAP client. The client responds by sending an encrypted response that indicates the authentication options that it has selected. The response is encrypted in such a way that proves that the client knows its password. The LDAP server then decrypts and verifies the client's response.
User Name: This property is used to specify the identity of the principal for authenticating the caller to the service.
Password: This property is used to specify the credentials of the principal for authenticating the caller to the service. By default, any text entered here is shown as asterisks (*), unless you turn off "Hide Password".
Protocol: The value of this property is a string that specifies the security protocol for the provider to use. The protocol is entered in the text box.
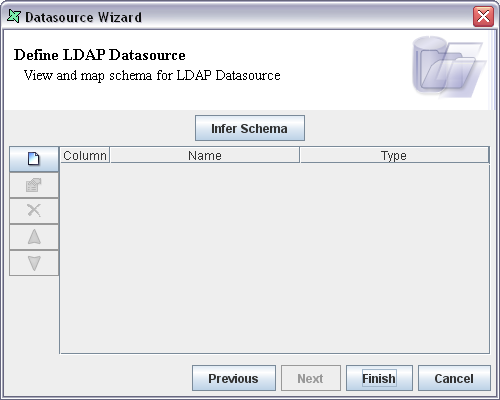
When you click on the Next button the screen appears as shown in Figure 11.3, “LDAP DataSource Schema”.
On clicking the Infer Schema button the settings you have entered so far are used to query the LDAP server and extract the schema attributes. The fields and the corresponding data types are displayed in the table. On clicking the Finish button in the data source Wizard the data source will be added to the repository.