Filter processor is a tool with which you can manipulate and group the database records to filter out those records which meet specific criteria.
In the Data Designer, the filtering can be done by using the built-in functions or using the Javascript function for more complex filtering. Multiple levels of filtering are supported, up to three filter conditions can be set for each field within a single processor.
The Filter processor is selected from the menu bar of the Designer window and then placed in the designer window workspace.
Properties
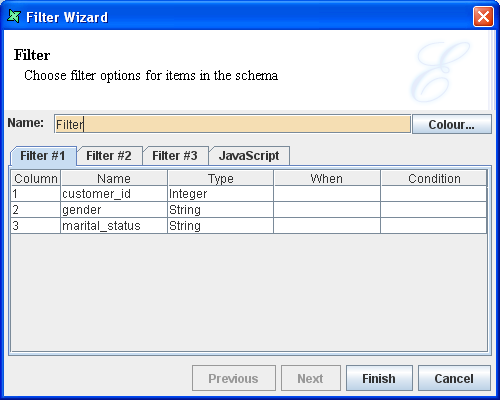
The editable properties are shown in Figure 4.28, “Filter Wizard”.
There are four tabs in the Filter Wizard: Filter#1, Filter#2, Filter#3 and JavaScript.
All the Filter tabs have the following columns:
Column - This column contains the row numbers.
Name - This column contains the field names.
Type - This column contains the data type of the records.
When - A combo box in each field from which the filter condition can be selected.
Condition - The filter value can be specified for the filter condition that has been set. You can also use dynamic parameters here to supply values at runtime.
All criteria entered on a Filter tab must be true for the record to be passed through. For example, using /ElixirSamples/DataSource/FruitSales.ds as the input to the filter, setting Filter #1 to read
- CompanyName Equals A
- Fruit Equals Apple
will ensure that only those records where CompanyName=A AND Fruit=Apple will be passed through.
However, any records not matched by Filter #1, may still be matched by Filters #2 or #3. Within a tab the rule is AND. Across tabs, the rule is OR. So if we enter in Filter #2
- CompanyName Equals B
we will get those records where (CompanyName=A AND Fruit=Apple) OR CompanyName=B. Therefore we will also get all records where CompanyName is B, regardless of the value of Fruit.
Table 4.1. Filter Criteria
| When | Condition | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
|
Type: Comparable types: String, Numeric, Date, Time, Timestamp Example: 10 1961-08-26 | This condition uses a simple comparison of values, which must both be of comparable types. For example, strings can be compared with strings, but not with dates. |
|
Type: String Example: US|Mex | This condition allows a regular expression to be used. Use of operators like "|" for OR and "&&" for AND relationship. This example will match USA or Mexico strings. |
|
Type: Numeric, Date, Time, Timestamp with "~" as separator Example: 1998-01-01~1998-12-31 | |
|
Type: Matching field type from another data source Example: See remarks |
repository:/Sample/DataSource.ds:Field1 This retrieves the matching field from another data source for filtering values. |
|
Nothing to enter |
Check whether if there is no content. Note that zero value is not considered null. |
|
Enter a script condition by specifying the matching type. Example: Field1==5|Field2=="US|Mex" where Field1 is numeric and Field2 is string. |
This is useful for enter multiple conditions or complex conditions using standard JavaScript. |
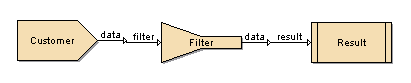
Add a new Composite DataSource named
Filter.Add the JDBC data source for Customer and Stores by dragging and dropping them over the Composite diagram.
Place the Filter processor on the diagram.
Connect the Customer data source to the Filter processor and connect the output of the Filter to the Result. The designer window appears as shown in Figure 4.29, “Sample Filter Flow”.
Filtering records by setting the When condition in Filter tab window
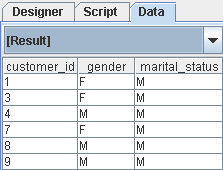
To start, let's filter the records of married customers with customer_id less than 11:
Open the Filter Properties and in the row corresponding to customer_id field select
Less Thanfrom the When column. Enter the condition as 11.In the Marital Status row select
Equalsfrom the When column and enter the condition as M. After setting the field properties the Wizard appears as shown in Figure 4.30, “Filter Result”.Click Finish button and review the Result data. Notice that only the records of married customers with customer_id less than 11 are shown.
Filtering records using the JavaScript functions
Now let's find stores in Mexico with store_id less than 10. For a change we will use JavaScript, though this can be solved just as easily with the Filter tabs.
Disconnect the Customer datasource and connect the Stores datasource to the Filter input.
Open the Filter Properties and remove any existing filter criteria. Then select the JavaScript tab window.
Enter the following JavaScript syntax:
store_id<10 && Country=="Mexico";
Note that because this expression is entered as a String, you can use dynamic parameters to customize the expression at runtime.Click the Finish button and review the Result data. Notice that the records corresponding to Mexico with store_id<10 are fetched.
Note
If in the above syntax instead of "&&" the "||" symbols are specified then all the records corresponding to Mexico and all the records having store_id<10 are fetched.